

new 4/10/03
|
Article No.
97-23-1 |
|
| Publication Date: NOVEMBER 10, 1997 | |
|
FORD:
|
1996-98 TAURUS |
|
LINCOLN-MERCURY:
|
1996-98 SABLE |
A comprehensive front suspension noise diagnostic and inspection procedure has been developed to aid technicians. The noise could be identified as any of the following: "clunking, popping, thumping, rattling, squeaking, or creaking."
Refer to the following Diagnostic and Inspection Procedure for details.
SOURCES OF VARIOUS FRONT UNDERBODY NOISES
Front underbody noises may originate from several different sources and are often difficult to locate and diagnose. Common noise locations include:
CUSTOMER ROAD TEST
Test drive the vehicle with the customer to understand the conditions that create the noise. The ability to duplicate the noise is a key step in Fixing It Right The First Time On Time. Once the conditions are established, you should then use an assistant to drive the vehicle while you direct your attention to defining the noise and locating its source.
DEFINING THE NOISE
When you hear the noise, properly defining it can help to determine the
source. Body and chassis noises are much like engine noises in that the type of
noise can help point to the suspect part. The type of engine noise helps locate
the source, such as a heavy, low knock being main bearing related, or a light
rapid engine knock being piston pin related. Defining the type of body and
chassis noise will help to identify possible sources as well as eliminate parts
that could not create the noise. A definition of common body and chassis noises
and examples are found in the following chart:
| NOISE | DEFINITION | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|
| Clunk | A clunk may be thought of as a loose part striking an adjacent part or solid surface. A clunk is often rhythmic, repeatable and metallic in nature. | A loose strut top nut may allow the strut to jump when going over bumps, possibly resulting in a repeatable clunk as the strut jumps. |
| Pop | A pop may be thought of as a secure part coming loose when force is applied to the part and then striking an adjacent part or surface. | A worn lower control arm bushing may pop as the brakes are applied. The weight of the vehicle holds the arm securely in the bushing until a greater force moves the arm and bushing, creating the pop. |
| Thump/Thud | A thump/thud may be thought of as a dull clunk as if a metal part is loose within a rubber bushing. | A worn sway bar bushing may create a thump/thud. An internal strut failure may also develop the same noise. |
| Rattle | A rattle may be thought of as a rapid light metallic noise. A rattle usually comes from a lighter part. | A bracket that has just begun to loosen may rattle, such as a loosened wire harness retainer, or a power steering cooler bracket. |
| Squeak | A squeak may be thought of as noise that results from two parts moving against each other. The noise can come from a metallic or rubber source. | A strut may squeak in the hub when turning if the lower pinch bolt is not securely tightened, or worn rubber bushing may squeak when flexed. |
| Creak | A creak is similar to a squeak, but shorter in duration, and is most likely from a metallic source. | A broken weld on a shock tower may creak over bumps, or a loose weld on the cowl may creak when turning. Creaks can often be duplicated when the vehicle is not moving by turning the wheel from stop-to-stop, jouncing the suspension, or by stalling the transaxle (power braking). |
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
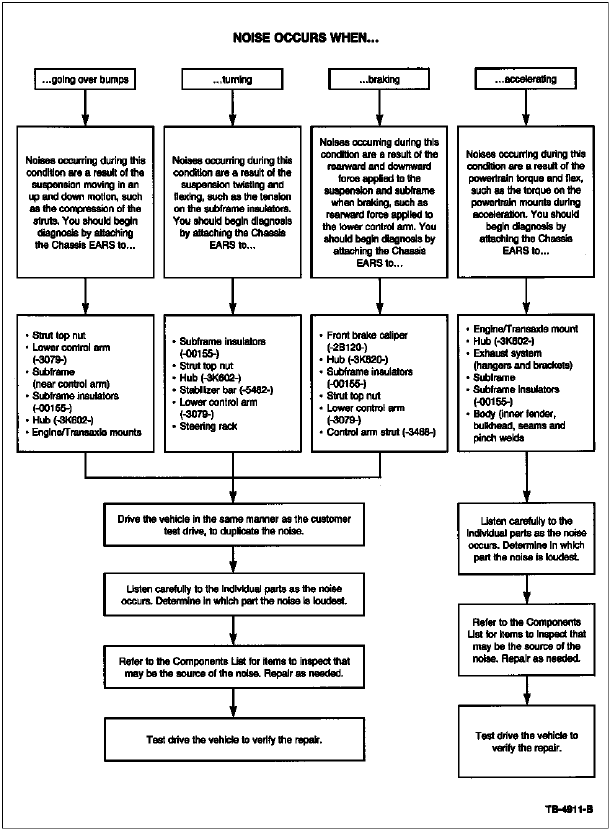
VEHICLE COMPONENT LIST
Refer to this Vehicle Component List for key items to inspect when a part has been identified as the most likely source for the noise. Inspect the part and perform repairs as needed. The type of noise possible from the part is identified within the () brackets and are as follows:
FRONT STRUT (S, GR)
Front Squeak And/Or Groan From Front Strut - Vehicles Built From 8/24/95-9/7/95 - TSB 96-3-3
FRONT STRUT (C, T)
Thump, Clunk And/Or Chuckle Noise From Front End Traveling Over Bumps - Vehicles Built From 6/19/95-5/10/96 - All Taurus/Sable Except SHO - TSB 96-13-1
BODY NOISE - (CR)
Creaking A-Pillar When Going Over Bumps And/Or Turning - Vehicles Built Through 12/31/96 - TSB 96-25-15
SUBFRAME MOUNTS (C)
Clunk On Heavy Accereration And/Or Deceleration Heard Or Felt In Floor Pan Area - Vehicles Built Through 2/28/97 - TSB 97-2-3
SWAY BAR LINKS - (C)
Clunking Noise From Front Suspension - Taurus/Sable Built Through 1/14/97 - TSB 97-2-5
96-13-1 , 96-25-15 , 96-3-3 , 97-2-3 , 97-2-5
INFORMATION ONLY
301000, 303000, 304000, 305000, 306000, 597997, 702000, 702100, 702300