Home | Mailing
List | Specifications | Care
and Feeding | Modifications | Vendors
| Literature

Fuel System, Described
WARNING:
DO NOT SMOKE, CARRY LIGHTED TOBACCO OR OPEN FLAME OF ANY TYPE WHEN
WORKING ON OR NEAR ANY FUEL-RELATED COMPONENT. HIGHLY FLAMMABLE MIXTURES
ARE ALWAYS PRESENT AND MAY BE IGNITED, RESULTING IN POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
Operation
An on-board vehicle powertrain control module (PCM):
-
receives inputs from various electronic engine control sensors to compute
the fuel flow rate necessary to maintain a prescribed air/fuel ratio
throughout the entire engine operational range.
-
outputs a command to the fuel injectors to meter the appropriate quantity
of fuel.
-
determines and compensates for the age of the vehicle and its uniqueness.
-
automatically senses and compensates for changes in altitude (for example,
from sea level to mountains).
All engines use a closed-type positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) system
and an exhaust emission system to control engine emissions to within government
specifications.
To maintain the required exhaust emission levels, the fuel delivery
system must be:
-
kept in good operating condition.
-
adjusted to specifications on the Vehicle Emission Control Information
(VECI) decal.
Additional engine performance checks are required to keep the exhaust emissions
at the specified minimum pollutant level.
The fuel delivery sub-system consists of:
-
a high-pressure in-tank mounted fuel pump.
-
a fuel filter/reservoir delivering fuel from the fuel tank through a 20-micron
fuel filter to a fuel injection supply manifold
-
the fuel injection supply manifold which incorporates electrically-actuated
fuel injectors mounted directly above each of the engine's eight
intake ports.
-
the fuel injectors which spray a metered quantity of fuel into the intake
air stream when energized.
A constant fuel pressure drop is maintained across the fuel injectors by
a fuel pressure regulator. The fuel pressure regulator is:
-
connected in series with the fuel injectors.
-
positioned downstream from fuel injectors.
Excess fuel supplied by the fuel pump, but not required by the engine,
passes through the fuel pressure regulator and returns to the fuel tank
through a fuel return line.
Fuel Injection Timing
For fuel injection timing:
-
Air entering the engine is monitored by flow, pressure and temperature
sensors.
-
The signals from the electronic engine control sensors are processed by
the powertrain control module (PCM).
-
The powertrain control module determines the needed fuel injector pulse
width and sends a command to the fuel injectors to meter the
exact quantity of fuel.
-
Each fuel injector is energized once every other crankshaft revolution
in sequence with engine firing order.
-
The period of time that the fuel injectors are energized (fuel injector
"on time" or pulse width) is controlled by the vehicle's powertrain
control module.
Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection (SFI)
The sequential multiport fuel injection (SFI) system is classified as
follows:
-
multi-point
-
pulse time
-
mass air flow controlled
Fuel is metered into each intake port in sequence with the engine firing
order according to engine demand through eight fuel injectors mounted on
a tuned intake manifold.
Air Induction System
The air induction system supplies filtered air to the engine to mix
with the fuel for combustion purposes and consists of the following:
-
air intake resonator
-
engine air cleaner (ACL) with air cleaner element (ACL element)
-
mass air flow sensor (MAF sensor)
-
air cleaner outlet tube
-
intake manifold with integral intake manifold runner control (IMRC) assemblies
Throttle Body
The throttle body has the following features:
-
controls airflow to the engine through a butterfly-type valve.
-
throttle position is controlled by a single lever and accelerator cable
linkage.
-
die-cast aluminum, single-piece body
-
a single bore with an intake air channel around the throttle valve. This
channel controls both cold and warm intake air control as regulated by
an idle air control valve (IAC valve) which is mounted to the surge tank
connector.
-
a throttle body-mounted throttle position sensor (TP sensor).
Idle Air Control Valve
The idle air control valve:
-
is an electro-mechanical device controlled by the powertrain control module
(PCM).
-
incorporates a linear actuator which positions a variable area metering
valve.
Intake Manifold
The intake manifold is made up of the:
-
intake surge tank.
-
LH and RH intake runners.
-
LH and RH air horns.
Runner lengths are tuned to optimize engine torque and horsepower output.
The entire intake manifold system must be removed to allow access to:
-
fuel injectors.
-
fuel injection supply manifold.
The intake manifold provides mounting flanges for the:
-
throttle body.
-
EGR valve (EGR valve).
-
EGR backpressure transducer.
-
intake manifold runner controls.
The unique air intake manifold features the following items:
-
an intake surge tank
-
LH and RH intake runners. The primary runner is always open. A secondary
runner is controlled by an electronically operated intake manifold runner
control (IMRC) deactivation motor and is open at high engine rpm.
-
vacuum taps for EGR valve, fuel pressure regulator, evaporative emission
canister purge and power brake booster are provided on the intake surge
tank.
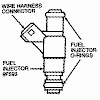
Fuel Injectors
The fuel injectors are:
-
electro-mechanical devices which meter and atomize fuel delivered to the
engine.
-
mounted in the lower intake manifold (IMRC) and positioned so that their
tips are directing fuel just before the engine intake valve.
An electrical signal from the powertrain control module (PCM) activates
the fuel injector allowing the fuel to flow. Since the fuel injector flow
orifice is fixed and the fuel pump pressure drop across the injector tip
is constant:
-
fuel flow is regulated by the length of time the solenoid is energized.
-
fuel is atomized by the director plate at the point where the fuel separates.
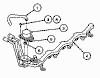
Fuel Injection Supply Manifold
The fuel injection supply manifold delivers high-pressure fuel from
the vehicle fuel supply line to the fuel injectors. The fuel injection
supply manifold consists of:
-
mounting flanges for the fuel pressure regulator.
-
mounting attachments which locate the fuel injection supply manifold and
provide fuel injector retention.
-
fuel inlet and outlet connections with push connect fittings.
A fuel pressure relief valve is located on the fuel injection supply manifold
for diagnostic tests and field service fuel pressure bleeding.
Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator:
-
is attached to the fuel injection supply manifold downstream of the fuel
injectors.
-
regulates the fuel pressure supplied to the fuel injectors.
-
is a diaphragm-operated relief valve in which one side of the diaphragm
senses fuel pressure and the other side is subjected to intake manifold
vacuum.
-
nominal fuel pressure is established by a spring preload applied to the
diaphragm.
-
balances one side of the diaphragm with manifold pressure to maintain a
constant fuel pressure drop across the fuel injectors.
-
bypasses and returns excess fuel to the fuel tank.
Fuel Pressure Relief Valve
The fuel pressure relief valve:
-
is used to relieve fuel pressure from the fuel system.
-
is located on the fuel injection supply manifold.
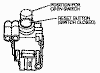
Inertia Fuel Shutoff (IFS) Switch
The inertia fuel shutoff switch (IFS switch):
-
is used in conjunction with an electric fuel pump.
-
shuts off the fuel pump in the event of a collision.
-
consists of a steel ball held in place by a magnet.
When a sharp impact occurs, the ball breaks loose from the magnet, rolls
up a ramp and strikes a target plate which opens the electrical contacts
of the inertia fuel shutoff switch and shuts off the fuel pump. Once open,
it must be manually reset before restarting the vehicle. The IFS switch
is located in the trunk along the right fenderwall, behind the trunk carpeting.
Usually identified with a white sticker.
Fuel Pump Relay
The fuel pump relay:
-
is integral to the constant control relay module.
-
supplies power to the fuel pump when the powertrain control module (PCM)
grounds the relay during starting and engine running conditions.
A/C Clutch Control Relay
The A/C clutch control relay:
-
is integral to the constant control relay module.
-
cuts off the A/C to improve idle smoothness after engine start-up.
-
cuts off the A/C to improve acceleration performance.
The A/C field coil is cut-off for approximately five seconds just after
the engine is started.
The A/C is also cut off when the throttle position sensor (TP sensor)
indicates a wide open throttle condition.
Contact Information


